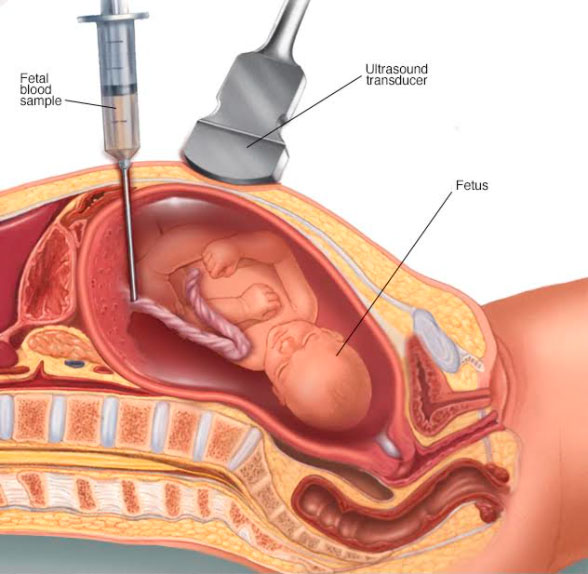
Percutaneous umbilical blood sampling — also known as cordocentesis— is a diagnostic prenatal test in which a sample of the baby's blood is removed from the umbilical cord for testing.
Cordocentesis is used primarily to detect and treat blood conditions, such as fetal anemia — a low amount of healthy red blood cells in a developing baby or for the diagnosis of fetal infections.
Cordocentesis is usually done when a diagnosis can't be made from amniocentesis, chorionic villus sampling, ultrasound or other methods.
Cordocentesis carries a higher risk of complications to the baby than other procedures do. Rarely, cordocentesis might be used to check fetal chromosomes through chromosome microarray or karyotype analysis. Blood obtained through cordocentesis can also potentially be used for other types of genetic studies.
Getting the test done is completely your choice. We can suggest what is good practice based on evidence-based medicine. Knowing all the pros and cons, you can accept or decline the testing.
Cordocentesis, which is usually done after week 18 of pregnancy, can be used to detect certain genetic disorders, blood conditions and infections.
The fetal medicine specialist will explain the procedure to you and offer you the opportunity to ask any questions that you might have about the procedure. You will be asked to sign few consent forms that gives the permission to do the procedure. There is no special restriction on diet or activity prior to chorionic villus sampling.
Your doctor will note if you are allergic to any medications, latex, iodine, tape, and anesthetic agents (local and general), medications that you are taking, any history of bleeding disorders or any anticoagulant (blood-thinning) medications, aspirin, or any other medications that may affect blood clotting. It may be necessary for you to stop these medications prior to the procedure. Your blood group will also be noted and if you are Rh negative, an injection anti-D will be given to you after the procedure.
An ultrasound will be performed to check the fetal heart rate and the position of the placenta and the fetus. The fetus is also assessed for structural abnormality. The procedure is done transabdominally.
Guided by ultrasound, the fetal medicine specialist will insert a thin, hollow needle through your abdominal wall into your uterus and into the baby’s cord. A small amount of blood from the vein in the umbilical cord will be withdrawn into a syringe, and the needle will be removed. An adhesive bandage will be placed over the abdominal needle insertion site. You'll need to lie still while the needle is inserted and the blood is withdrawn. You might notice a stinging sensation when the needle enters your skin, and you might feel cramping when the needle enters your uterus.
You are made to rest for half an hour after the procedure. The fetal heart beat is checked and then you are sent home. Most women have no problems, but you might have a bruise, spotting or cramping. If you do, paracetamol is safe to take. If you have a persistent pain, leaking, bleeding or a high temperature, then you need to go to the hospital.
However, besides, these there is increased risk of bleeding from the cord puncture site or formation of hematoma at the puncture site. There is possibility of slowing of fetal heart rate and fetal loss rate is 1-2%.
There is minimal risk of miscarriage or infection after the procedure.